this post was submitted on 14 Jan 2024
641 points (97.6% liked)
Greentext
4452 readers
520 users here now
This is a place to share greentexts and witness the confounding life of Anon. If you're new to the Greentext community, think of it as a sort of zoo with Anon as the main attraction.
Be warned:
- Anon is often crazy.
- Anon is often depressed.
- Anon frequently shares thoughts that are immature, offensive, or incomprehensible.
If you find yourself getting angry (or god forbid, agreeing) with something Anon has said, you might be doing it wrong.
founded 1 year ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments
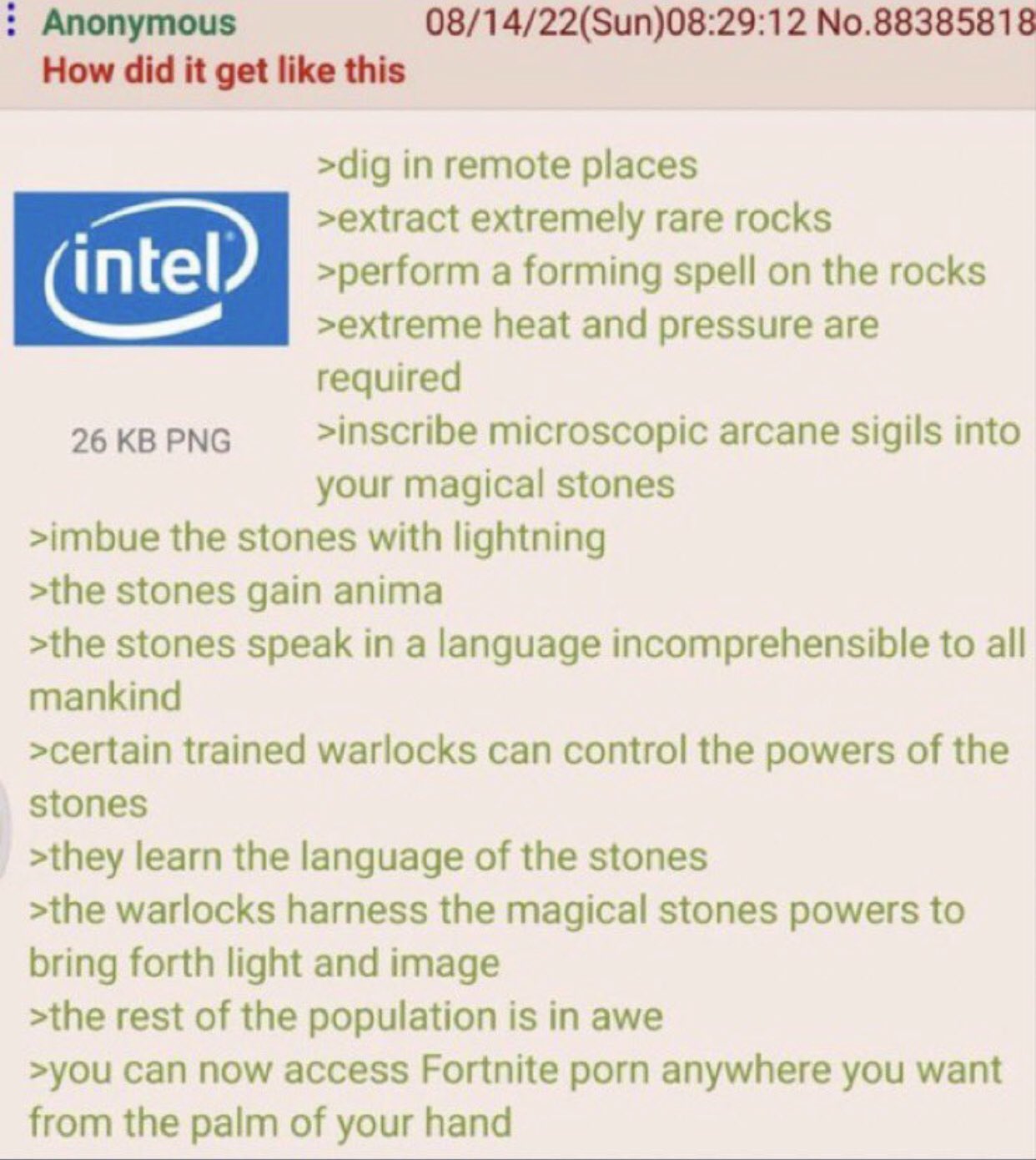
"extremely rare" is a way of saying second most common that I haven't heard before.
The rare stone thing would be better for nuclear power. Find lots of rare stone, put it together in a huge pile, they get warm and cause mysterious diseases.
Uranium is actually pretty common, refining out the right isotope is the complicated part. Heck there were a couple natural nuclear reactors in a place that generated power for a few million years.
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Natural_nuclear_fission_reactor
Isn't uranium that's pure enough naturally to cause a reaction on its own really rare? I'm referring to the Chicago Pile experiment. It was so simple that it could have been theoretically built thousands of years ago which is crazy to think about.
Not really. Every single shovel full of dirt has trace amounts. It's just gathering enough into a pile. Like I said, nature did it on earth, before humans existed. It's weapons grade uranium that's really rare
You can't get a reaction when it's that trace though. It needs to be unusually pure to be able to stack a bunch of raw ore and get a reaction.
Nature did get the reaction with no humans. I don't know what to tell you
Silicon is just the base material. The whole process involves a whole bunch of other chemicals, and some of those are made of much rarer stuff than silicon.
Sure, Silicon works as a cheap base. Boron, phosphorus, arsenic and antimony are also used in the process, though. Other elements are also finding use in the process.
There is also a minor error in the middle about the 'sigils'. When scribing process is happening, the other elements are embedded into or deposited onto the substrate between 'scribings'.
I don't think they mean silicon, I think they mean gold, which is also a crucial component to electronics.
Gold also isn't all that rare. It's value is so high because of jewelry marketing, not rarity.
Gold is rare, compared to just about every other element, in accessible areas of earth. All the gold ever discovered on Earth would fit inside a 23 meter (75 foot) cube. This is about 244 thousand tons, in all of human history.
Compare this to iron, where just the United States produces 46 Million tons in 2022 alone.
There is plenty of gold deep within the Earth - it is very dense, so it sank towards the core when Earth was recently formed - but on the surface and the proximal crust, it is not found in abundance.
Is that 23mx23mx23m or 23 cubic meters?
The first one, 23x23x23
Those...Are the same thing?
Edit: I thought they meant 23x23x23 as in dimensions not multiples
23x23x23 is 12167 cubic meters.
Okay I see where I fucked that up
That is a mind blowing fact about all gold fitting in 23 cubic meters. I had to fact check it because it sounds so absurd: https://www.bbc.com/news/magazine-21969100
You may be confusing with diamonds. Gold is, and in fact, any element heavier than iron are pretty rare because they cannot be created by stars alone according to current models, they need more extreme and rare astrophysics phenomenons like supernova and black holes.
Yes I think that is the exact confusion I had.
Technically correct but just cause there are minerals in the ground doesn’t mean they can be extracted.
Maybe i am wrong but i keep hearing about silicon being harder to come, i suppose op was specifically speaking about the silicon usable for computing.
interesting silicone usually makes it easier for me to come
The form of silicon used in semiconductor manufacturing, specific formations of sand, is becoming harder to source from the environment. Silicon the element is incredibly abundant - the vast majority of all rocks on Earth are silicates - so there isn't a risk that we run out of silicon itself any time soon.
What may happen, in several decades, is an increase in price due to the need to process more abundant rocks to obtain pure silicon.